Thermal transfer printing is often referred to as TTR printing. It involves the transfer of ink from a TTR ribbon to a substrate through a heated print head. Unlike other technologies like inkjet or direct thermal, TTR technology offers exceptional durability. This makes it ideal for applications that require lasting prints like best-by dates, batch information, and other variable data.
To get started in finding the most suitable TTR ribbon, we will explore the specifics of TTR technology, formulations, and sizes. Additionally, we’ll also address the key factors that influence your ribbon selection process.
Throughout this article, we’ll explore important questions such as: What are your application requirements? What material will the TTR print be applied to? And what type of printer are you using – flat-head, near-edge, or TTO? By considering these factors, we’ll help you explore the vast array of options. So that you can find the perfect TTR ribbon that meets your unique needs.
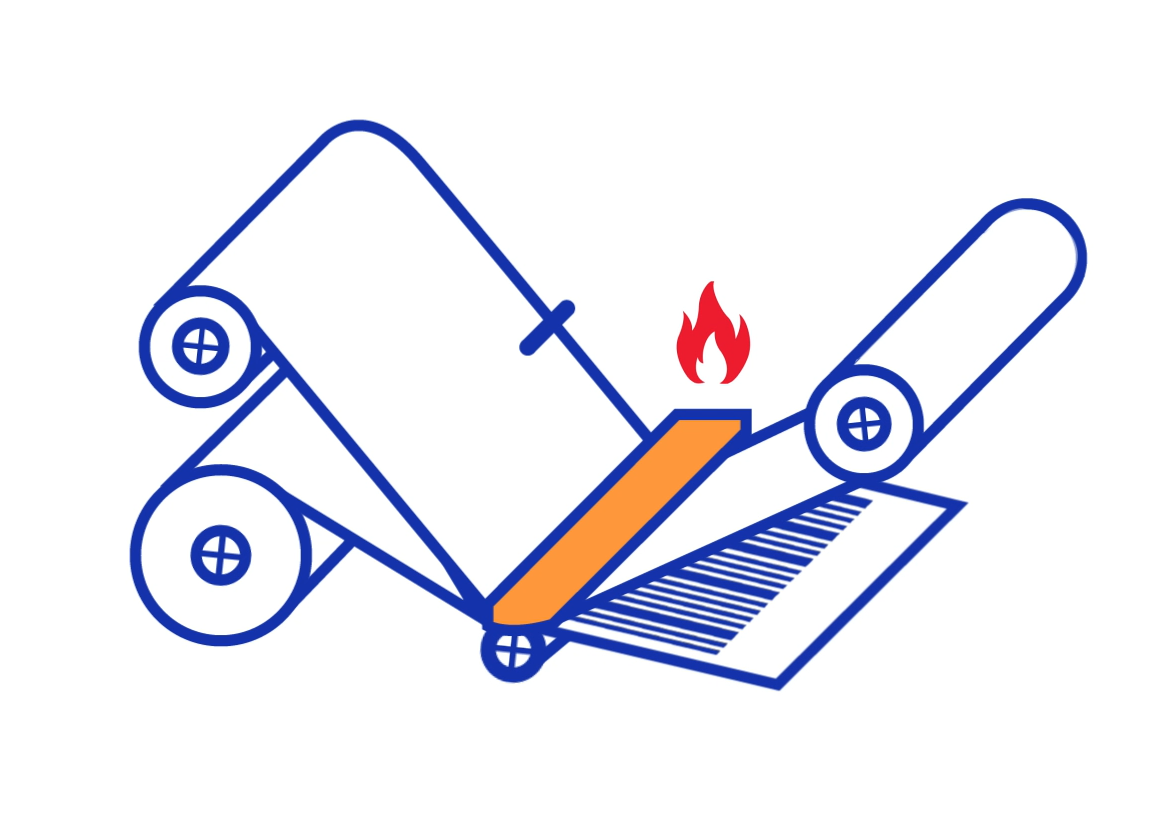
The specifics of TTR printing
Thermal Transfer Printing is a technology, where an image made by a TTR Printer appears on a selected substrate. This happens when the ink from a TTR ribbon contacts a heated print head and transfers onto a substrate, for example, a label.
Heat from the print head melts the ink on the ribbon and releases (transfers) the ink directly onto the substrate. TTR technology uses a special ribbon, often shortened to TTR. This thermal transfer ribbon comes in many different formulations and sizes. Formulations can contain resins, wax, or a mixture of both. Depending on the TTR printer and the application, there are special formulations to address your application requirements such as longevity or potential exposure.
Obtaining durable prints with TTR technology
TTR printers are widely used for obtaining durable prints. Particularly, for variable information, such as barcodes, best-by dates, and batch information. While inkjet and direct thermal technologies are also commonly used for variable data printing, TTR technology is preferred when are more durable, resistant print is required.

To give some examples: for cash receipts and logistical labels or short-time deliveries one more often than not uses direct thermal or inkjet technology. However, when a logistical label should be readable for a longer time, such as with ocean/container freight, TTR printing becomes the more durable option.
Three factors to consider to identify the most suitable TTR ribbon type
From the moment TTR technology becomes the best option, there is a wide range of factors that will determine the most suitable TTR ribbon. To determine the correct choice, you should answer 3 main questions:
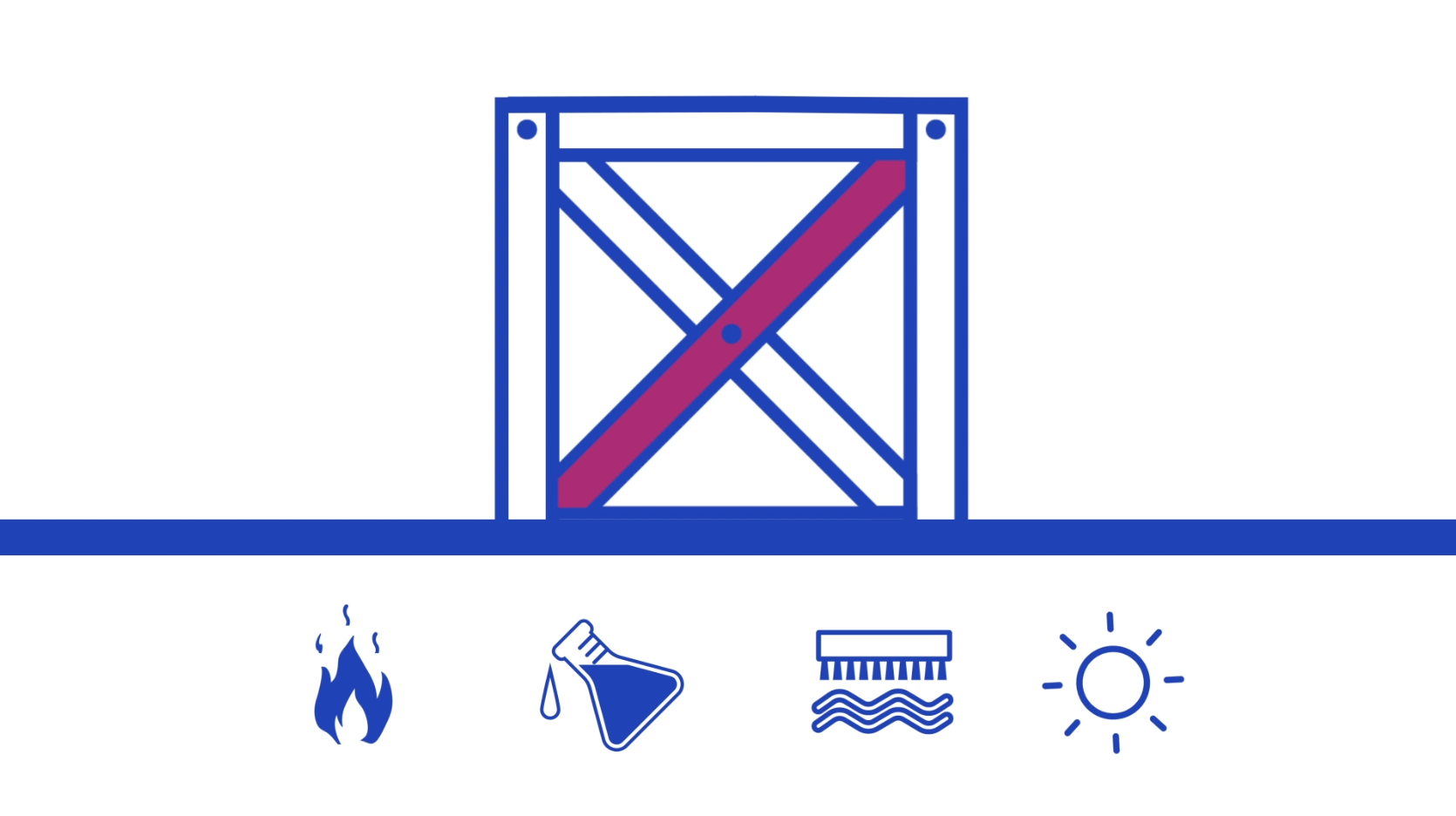
- Application requirements: Understanding the specific requirements of the application is essential. Factors such as resistance to environmental conditions, durability, and shelf life are crucial considerations. For example, if the printed labels will be exposed to harsh weather conditions or chemicals, you may need a more resistant TTR ribbon, such as a resin ribbon.
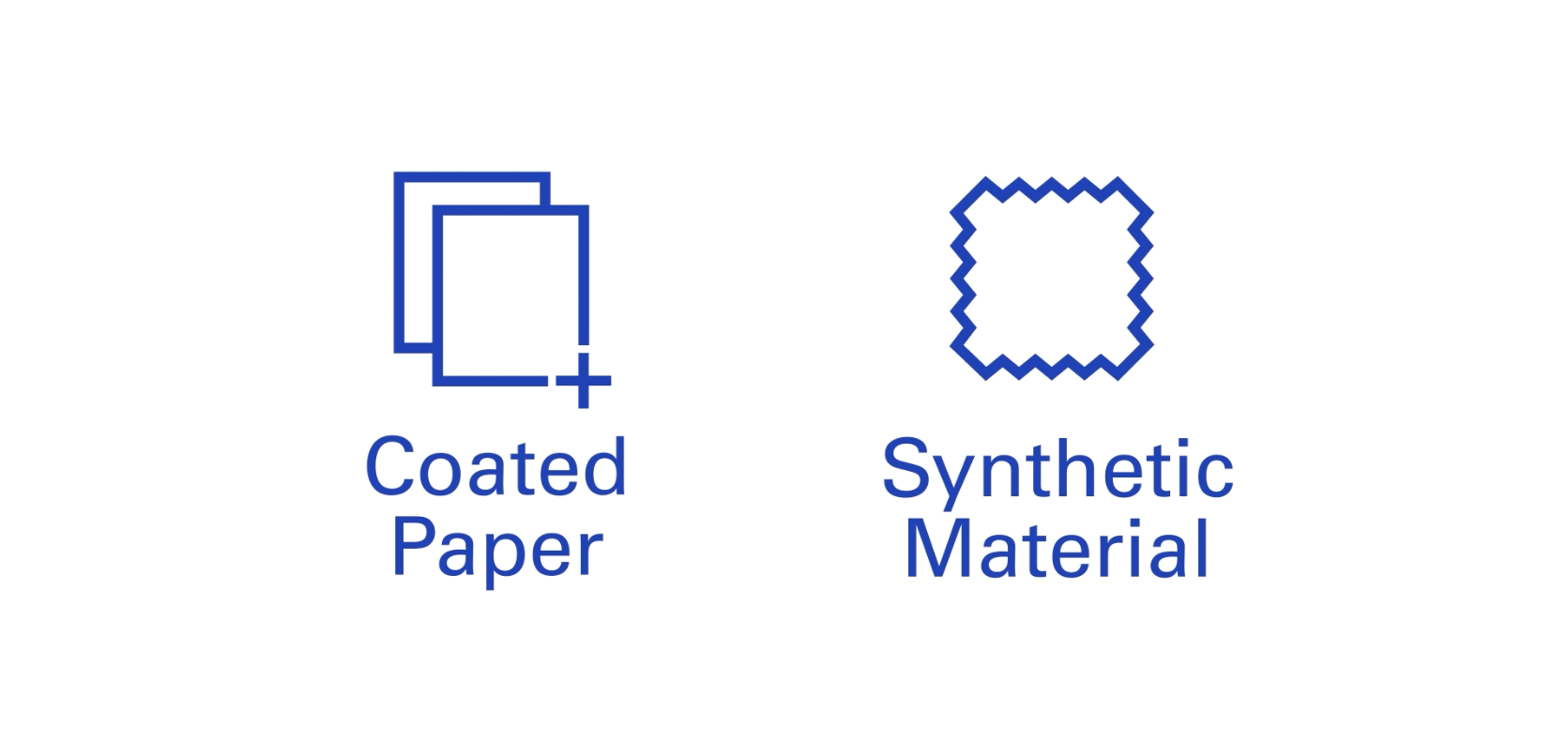
- Substrate/Material: The type of substrate or material on which the TTR print will be applied plays a significant role in selecting the appropriate ribbon. Different materials may require different ribbon formulations to ensure optimal print quality and adhesion. For instance, printing on glossy paper might require a different ribbon type compared to printing on synthetic materials like polypropylene or polyester.
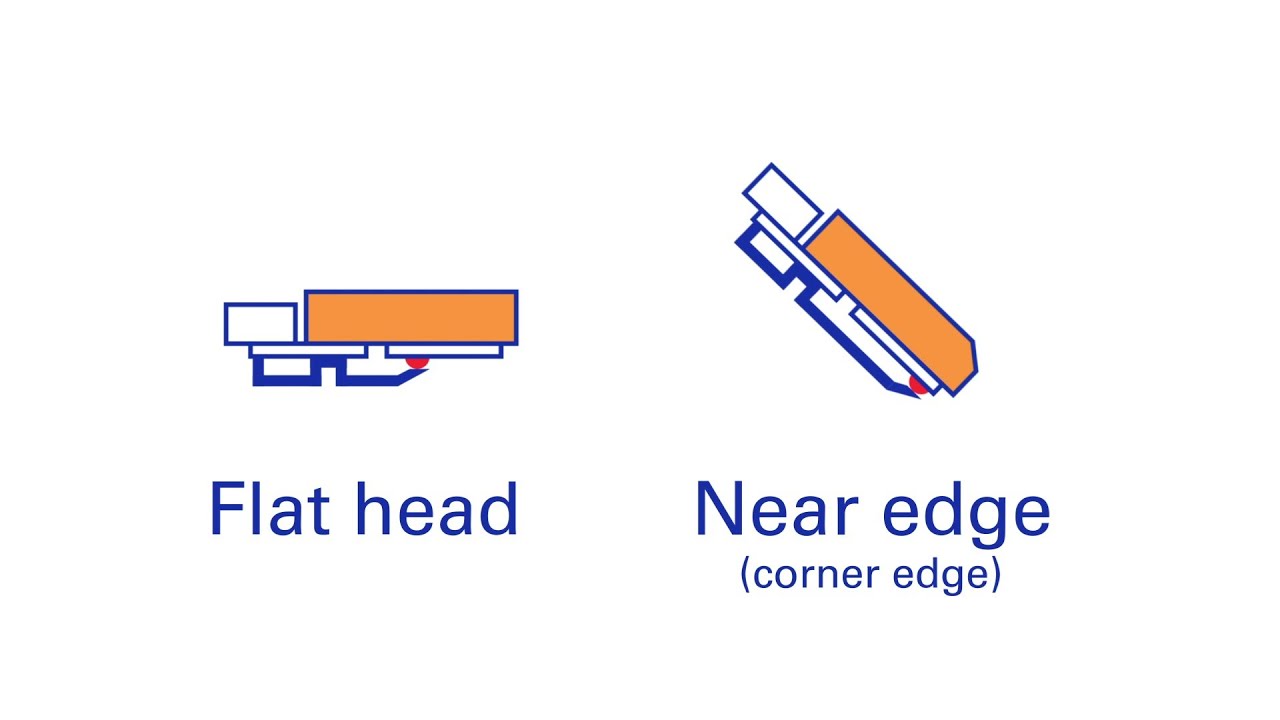
- Printer Type: The type of printer being used, whether it is a flat-head, near-edge, or thermal transfer overprinter (TTO), also influences the choice of TTR ribbon. Each printer type has specific requirements and compatibility with certain ribbon types. It is crucial to select a ribbon that is compatible with the printer to achieve optimal printing results.
The choice of TTR ribbon will be the result of the combined answers.
Defining the application requirements
This is the most important step as it helps in narrowing down the options and excluding certain TTR ribbon formulations that may not meet your specific criteria.
Some important factors to consider are the desired longevity and potential exposure of the printed information. Imagine this: you have a print that should survive a long trip on a carton box with harmless content. Or perhaps, you need the print to withstand being immersed in the contents of the leaking container of chemicals it is applied to. These scenarios call for drastically different ribbon types, and that’s where defining the application requirements becomes crucial.
The below list works as an example to show the type of input that helps determine the exclusion of certain TTR ribbon types
- The time that the information should be readable for
- The substances the print can be exposed to
- The amount of abrasion and/or scratching
- The temperatures (high/low)
- The amount of sunlight
- The degree of humidity
- Food contact
- Certifications (ISEGA, RoHS, etc.)
Once this information is available, it becomes apparent whether a wax TTR ribbon is sufficient or that a wax/resin or even a resin is needed to secure the required readability and survivability of the print.
Determining the substrate/material to be printed
The information from the previous step is also key in determining which substrate/material you should use for TTR printing. Both the TTR print and the material need to have the same requirements in terms of durability and exposure to get the desired result.
There is a wide variety of substrates on the market ranging from paper to synthetic materials, each intended for specific industries and applications. For example, if you need the printed information to be readable after repeated or long-term exposure to water, a simple paper label will not be a suitable choice.
Another important factor in choosing a proper TTR ribbon is the surface of the material: is it rough like uncoated paper or smooth like vinyl? This factor plays a significant role in determining the best ribbon formulation.
Ribbons containing wax components are more suitable to print on rough surfaces as the wax will melt into uneven parts of the label. This ensures that enough ink is available above the surface of the label, ensuring a crisp, dark print. On the contrary, for very smooth surfaces, an adhesive is needed in the formulation to secure the print to the substrate, here resin TTR ribbons have an advantage. Their formulation contains an adhesive that is activated by the heat of the printhead in the TTR printer.
With the material selection in hand, it is time to move on to the next step – choosing the right printer.
TTR printing on flat-head, near-edge, or thermal transfer overprint (TTO)
TTR printing can be done using flat-head, near-edge, or thermal transfer overprint (TTO) printers. Different TTR printers require different TTR ribbons, depending on the type of printhead. There are two types of printheads: flat-head and near-edge:
- Flat-head printers are desktop or industrial stand-alone printers, that produce prints that are later applied on the final application. Flat-head printers are generally printing somewhat slower and can produce the most durable prints, due to a longer exposure time of the label and TTR ribbon to the heated printhead.
- Near-edge printers, on the other hand, are both used in industrial stand-alone printers as well as in-line TTO printers. These print heads enable higher printing speeds that require specific TTR ribbons. Especially the very high speeds of TTO printers have high demands on the release speed of the ink on the ribbons, requiring specific quick-release layers in the formulation.
When a TTR printer is already available, the choice of TTR ribbon is a result of the selected substrate and the application requirements. When you still need to acquire a TTR printer, it is best to check the application requirements beforehand. This is, for example, important when you need an extremely durable print. In this case, it could be the best choice to opt for a flat-head printer which can print with the most durable resin TTR ribbons.
When know your application requirements, substrate, and printer, it is time to move on to the next step: testing and determining the correct printer settings. This will ensure optimal printing results and help achieve the desired outcome.
Testing the combination of substrate, TTR ribbon, and printer
Fine-tune your TTR printer settings
Testing is a combination of finding the correct settings of the printer and conducting tests to evaluate the print results according to your application requirements.
Both the suppliers of TTR ribbon and TTR printer should be able to provide you with the standard recommended settings for a specific type of ribbon. From this starting point, you can fine-tune the settings to get the optimal print result for further testing.
You can generally change your TTR printer settings according to the following parameters:
- Print speed: You can increase or decrease the print speed. Too high speeds can lead to the quality of the print to deteriorate
- Print heat: You can increase or decrease heat to properly apply the ink/adhesive to the substrate. Too high heat settings can cause printhead wear and higher energy consumption
- Print pressure: You can apply more or less pressure by the printhead. In general, thinner substrates require more pressure.
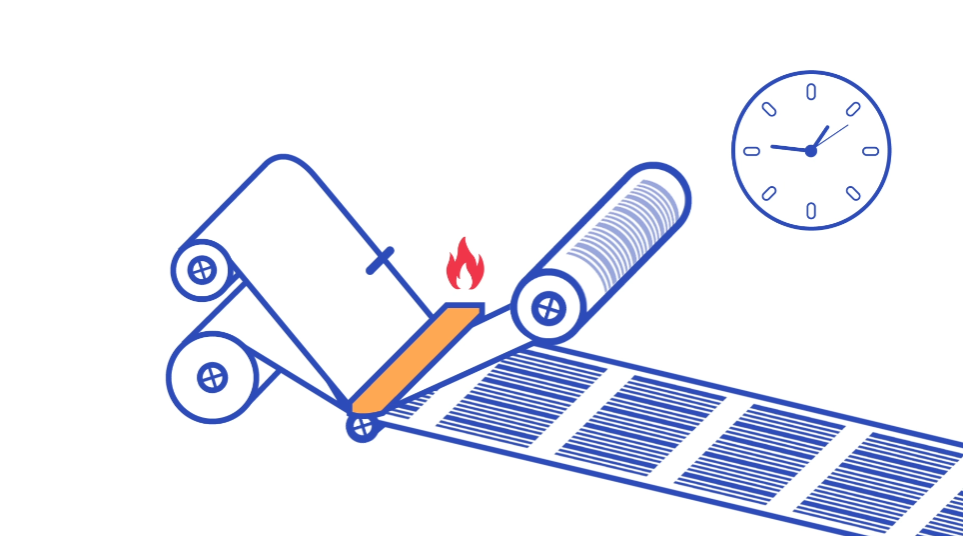
Delve into manufacturer guidelines and ask for expert advice
Guidelines for fine-tuning to find the most optimal settings differ between TTR ribbon types. For wax ribbons, you can often at the recommended settings and increase speed until the print quality starts deteriorating. Meanwhile, for resins, you would often decrease the print heat from the recommended settings until the print result becomes unsatisfactory.
When you are happy with the quality of your prints, you can move on to testing them against the application requirements. This can, for example, include a scratch test with a coin and a wiping test with a cloth soaked in a certain chemical.
For many tests, the manufacturers of TTR ribbons, printers, and substrates have standardised test protocols and equipment. Check what facilities your suppliers have available to support you with the testing. Some suppliers also offer on-site support to help you achieve quality results.
Once you have found the proper settings, and the print has survived the necessary tests, you are all set!

So how do you find the most fitting TTR ribbon for your situation?
In conclusion, finding the right TTR ribbon is crucial for achieving optimal TTR printing results. By considering key factors such as application requirements, substrate type, and printer type, you can ensure that you select the most suitable thermal transfer ribbon for your specific needs.
Remember to assess the durability, print quality, and compatibility of the ribbon with your printing equipment to achieve lasting and high-quality prints. Additionally, don’t hesitate to seek guidance from our TTR experts. At DNP, we offer tailor-made advice when it comes to harmonising your substrate, printer, and ribbon. Do not hesitate to get in touch with us if you require technical support in our DNP lab or on-site, in your production environment.
