What are common techniques for the printing of variable data?
Direct thermal vs Thermal Transfer Printing are two common techniques for the printing of variable data such as barcodes and batch information.
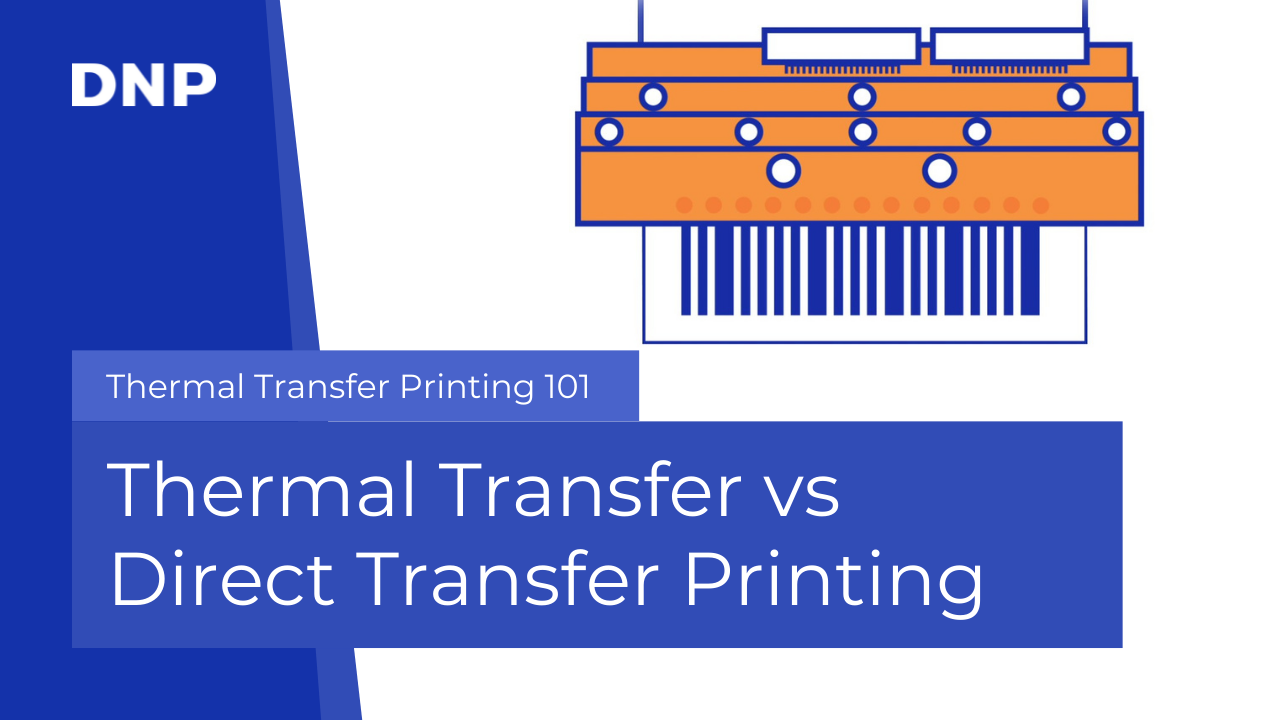
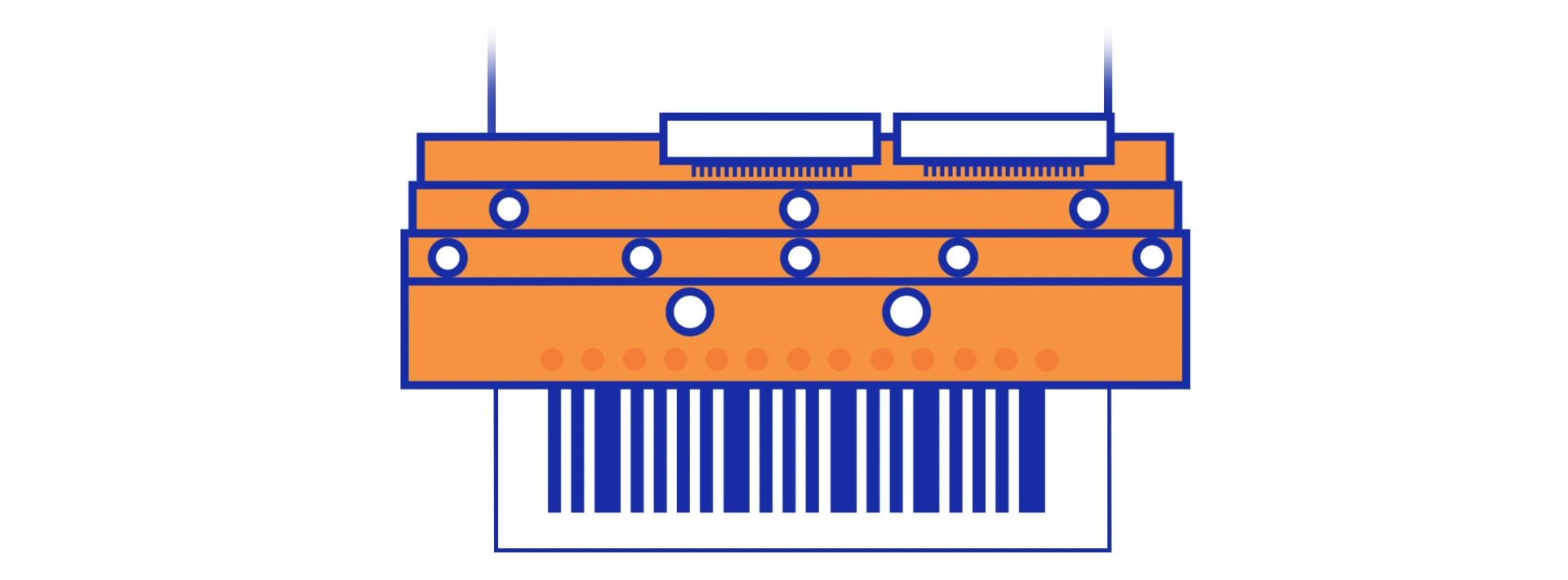
Both printers use a heated print head to create the image on the substrate. These print heads consist of many tiny elements or dots that heat up individually and shape the image.
All in all, thermal label printers are considered to be an ideal choice for variable data printing, thanks to their ability to print high-quality images with excellent edge definition. Both direct thermal and thermal transfer printers are designed to print accurately with the exact bar widths that quality coding and scanning require.
Direct thermal printing vs thermal transfer printing – What’s the difference?
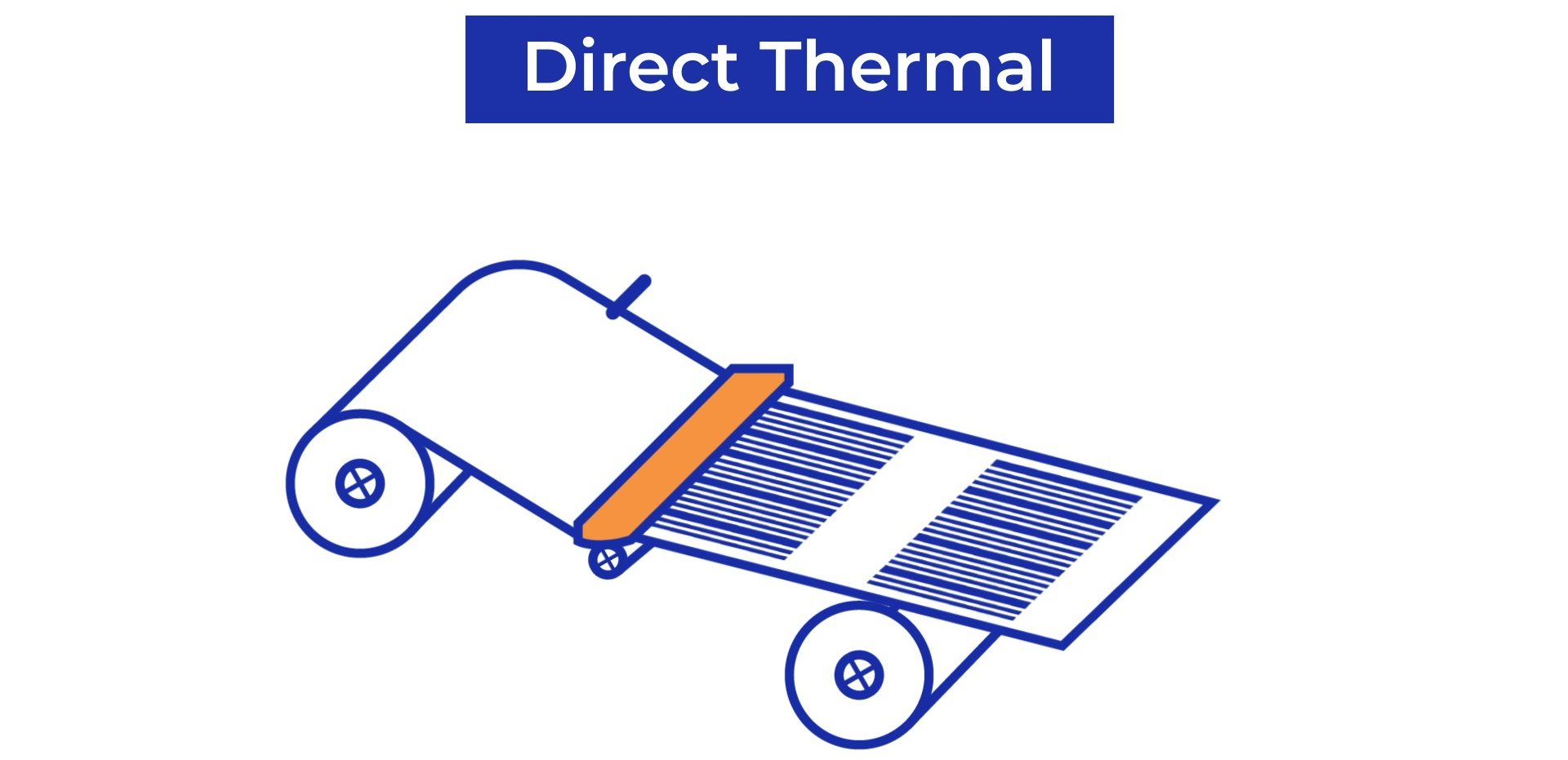
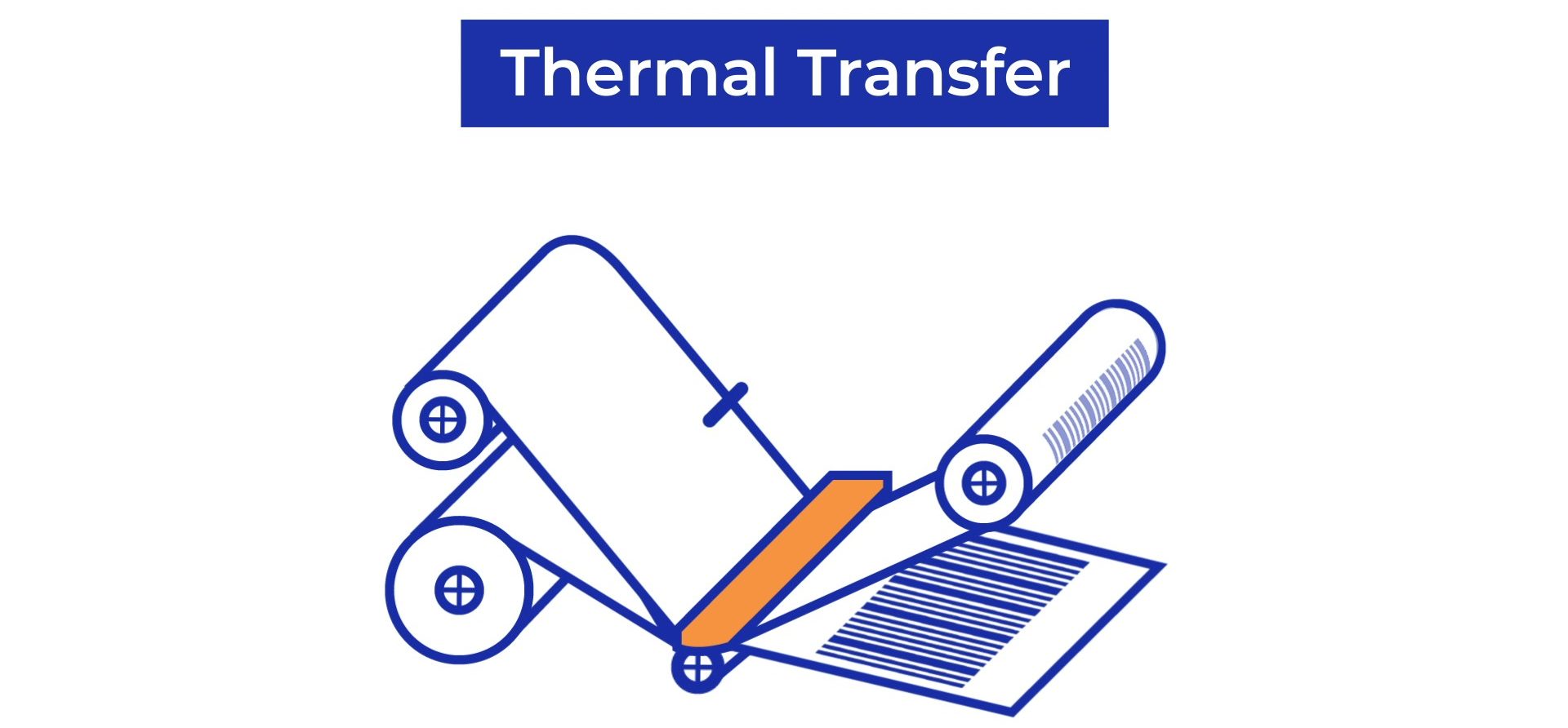
One major difference between Direct transfer vs Thermal Transfer printers is the use of ink ribbons. In Thermal Transfer Printers, the print-head uses heat to transfer the ink from the ribbon and prints this onto a wide variety of substrates such as a PP or PE label material. On the contrary, direct thermal printers only use a special, chemically treated, heat-sensitive label material. In this case, the print-head uses heat to activate the thermal label material and to change the colour from white to black.
But the two technologies also drastically differ when it comes to durability. While direct thermal printing is more common for less durable applications, thermal transfer printing is famous for excelling in long-life printed data.
What do you need to know about direct thermal printing technology?
Direct thermal printers print data without the use of an ink ribbon or toner, making them rather simple to operate. In general, labels used for direct thermal printing have a relatively long shelf life. However, certain environments such as exposure to heat, abrasion, or long periods of direct sunlight could decrease this shelf-life drastically.
When the label is exposed to heat, the material will darken and previously printed text or barcodes will fade and no longer be readable. This is exactly the reason why direct transfer printing is used for information that only needs to be available for a shorter period. For instance, you can come across direct transfer printed data when you get your receipts at the grocery store or at shorter logistical chains like shipping labels, patient and visitor identification, and ticket printing.
What do you need to know about thermal transfer printing technology?
Thermal transfer printers are often used for long-lasting prints that must be durable against heat, chemical abrasion, and other exposures. For example on car parts, chemical containers, and longer logistical chains.
The clarity of images printed with Thermal Transfer technology is provided by the use of a heated print head that melts ink from a Thermal Transfer Ribbon onto a substrate such as a label.
When Thermal Transfer Ribbons are carefully matched with the correct substrate and printer settings, the technology provides a print that can perform well against heat and moisture, as well as certain chemicals or exposures to sterilisation, or cryogenics processes. This technology also creates images that perform well against frequent handling such as rubbing, smudging, or scratching, making the printed image one of the most durable ones currently on the market.
Typical applications for thermal transfer printing include product or product part identification, inventory tracking, packaging information on, for instance, medical devices, laboratory item tracking & tracing; and best-by dates on food & beverage products and cosmetics.
What are the main advantages of each thermal printing technology?
Direct thermal vs thermal transfer: two technologies serving similar purposes for different applications. Both technologies have their own additional advantages.
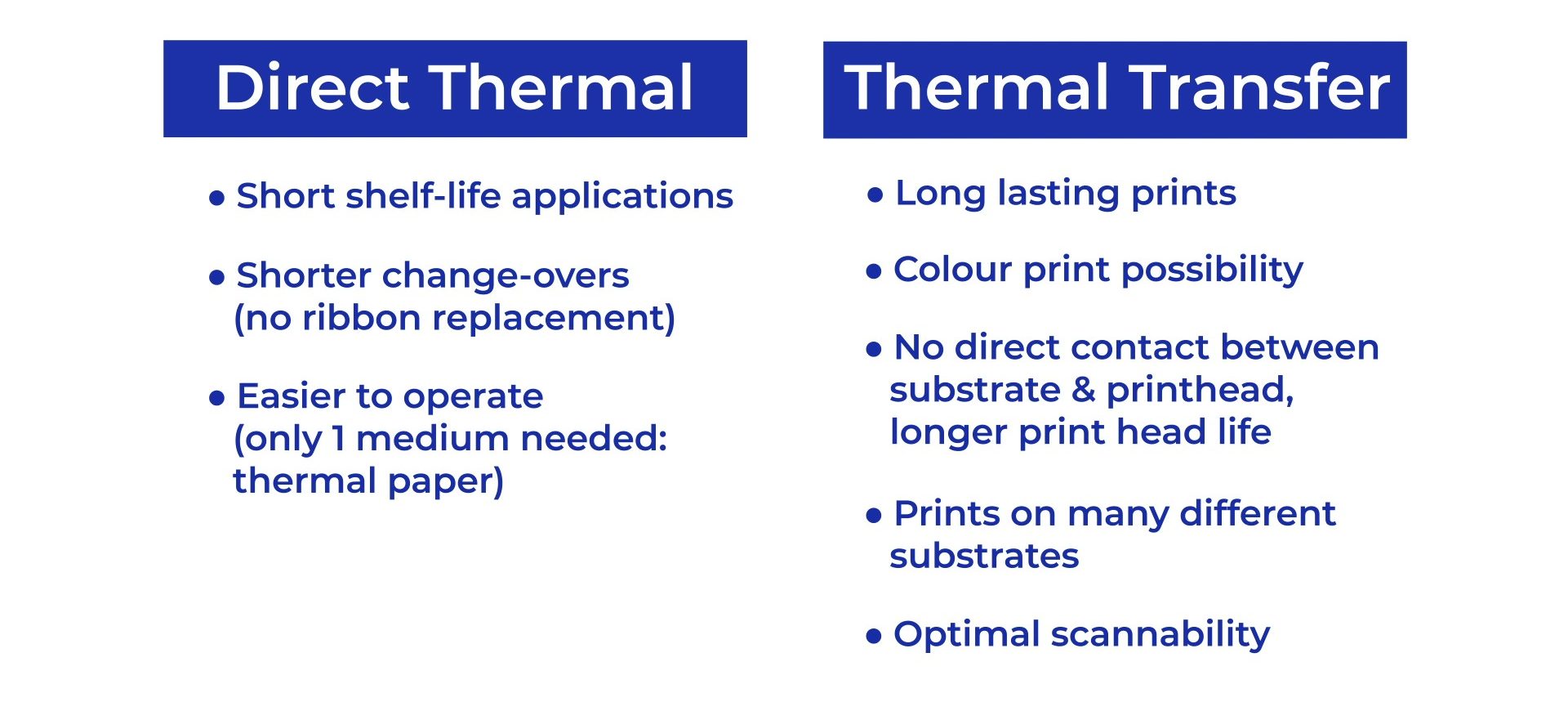
Advantages of direct thermal printing:
- Direct thermal printing creates sharp, quality prints that are easy to scan
- The use of direct thermal printers is easy, with no need for toners, ink, or a thermal transfer ribbon
- Direct thermal is ideal for applications requiring only a short shelf life
- With no supplies to replace other than the direct thermal label, change-over times are shorter than for other printing technologies
Advantages of thermal transfer printing:
- Thermal transfer printing delivers long-life printed image stability.
- Thermal transfer printing produces sharp, high-definition text, barcode, and other images delivering maximum readability and scannability.
- Thermal transfer technology can print on a wide variety of media stock from vellum, to aluminum, PE, PP and PET.
- Long-term maintenance costs are low compared to ink jet and laser printers
- With proper care and ribbon selection, thermal transfer printheads last longer than direct thermal printheads
Limitations of direct thermal printing:
- Direct thermal printing is not meant for long-term applications
- The print is extremely sensitive to environmental conditions such as heat and light
- After printing direct thermal paper remains chemically active. Often therefore such tags and labels are top-coated to attain higher durability.
- Thermal transfer printheads often last longer than direct thermal printheads increasing long-term maintenance costs
Limitations of thermal transfer printing:
- Requiring a Thermal Transfer Ribbon, as well as a substrate to print on, the costs of consumables are higher than direct thermal
- To deliver optimum print quality with thermal transfer printing, the ribbon, substate and printer settings need to be compatible. This requires expert knowledge and/or more trial and error. Tailored service from a trusted manufacturer can help you on your way to find the correct match and enable you in delivering variable print excellence
- With no ribbon saving feature on the printer, thermal transfer ribbons can be wasteful if little is printed on it
- Thermal transfer ribbons are difficult to recycle due to the ink coated on the basis PET film – Using a ribbon saving feature on your thermal printer or a thinner ribbon can help in reducing plastic waste
In a nutshell, direct thermal printing can help you with short shelf-life applications, whereas Thermal Transfer Printing is the preferred technique for quality, long-lasting prints.
Do you have any additional questions? Or wonder if Thermal Transfer Printing is the best choice for your needs? We are here to help in providing tailored support that best fits your needs!